Military Coup in Gabon August 2023

Summary of Military Coup in Gabon
In the early hours of 30 August, the Gabonese Election Centre (CGE) announced that President Ali Bongo had won a third term in office, having received 64.27 percent vote share in Saturday’s general election. However, just after 05:00 local time, a group of senior officers from the Gabonese military announced on television channel, Gabon 24, that they had seized power with the full support of the Gabonese security and defence forces.
Introducing themselves as members of The Committee of Transition and the Restoration of Institutions, the officials stated that the election results were cancelled, all borders were closed until further notice and state institutions – the government, the senate, the national assembly, the constitutional court and the election body – were dissolved.
Following the announcement, domestic and regional sources reported gunfire could be heard in the capital Libreville. However, as the day progressed, the streets appeared calm, and crowds of citizens peacefully took to the streets. Videos circulating on social media showed multiple instances of people celebrating and cheering, often in close proximity to the country’s armed forces. So far, there has been no signs of widespread protest or alarm. Several hours after the officers’ announcement, internet access also appeared to be restored for the first time since Saturday’s vote.
The Gabonese government has yet to make an official statement, with President Bongo reportedly under house arrest, surrounded by his family and doctors.
Potential for Political Unrest in Gabon
Ahead of the coup, there was significant concern over potential unrest following Saturday’s presidential, parliamentary and legislative elections that the opposition alleged were plagued by fraud. Questions over the election’s transparency were re-enforced by the lack of international observers, the suspension of foreign media broadcasts, the decision to cut internet service, and the imposing of a nationwide curfew.
President Ali Bongo and his father, Omar Bongo, have ruled Gabon since 1967, but frustrations with the political dynasty had been growing for several years ahead of Saturday’s election. The Central African nation is a major oil producer, so much so that it is a member of OPEC, as well as being a major exporter of uranium and magnesium. Indeed, the country is home to over one-quarter of the world’s proven magnesium reserves. However, Bongo has done little to channel its oil and other wealth towards the population of some 2.3 million people, a third of whom live in poverty.
This is also not the first attempt in recent history to overthrow Bongo as in January 2019 he and the Gabonese government were able to foil an attempted military coup after soldiers briefly seized the state radio station and broadcasted a message saying Bongo, who had suffered a stroke months earlier, was no longer fit for office.
Find further analysis on political instability in West Africa
Situation Analysis by Solace Global
The strength of Gabon’s extractive-based economy means that it is Africa’s third most wealthy country by GDP per capita. However, with large swathes of the country still living in poverty, it is highly likely that the state has failed to transfer much of this wealth to ordinary citizens. It is likely that economic disparities have been one of the major triggers for the coup. This is likely supported by the lack of public resistance and the fact that celebrations have been seen on the streets of Libreville and other major population centres across the country.
Furthermore, the coup has yet to be characterised by anti-French rhetoric in a similar vein to the recent West and Central African coups in countries like Niger and Mali. However, the coup is almost certainly another problem for Paris in Africa, with multiple French companies operating in the country. Unlike the other coups in Africa, it is doubtful that the Gabonese coup leaders will seek Russian support in favour of maintaining Western relations. Gabon has traditionally had weak ties with Russia and unlike much of Africa, has not been threatened with major insurgencies and security issues. Moreover, Gabon was one of the countries in Africa that voted against Russia at the United Nations in the 2022 resolution on Ukraine.
Economically, the coup is almost certainly going to lead to price volatility in global oil and magnesium markets. Gabon has strong economic links with both France, and increasingly with China, and it is a major exporter of commodities to these nations. Reports indicate that some foreign companies like the French mining company, Eramet, have already suspended operations in Gabon in response to the coup. It is therefore highly likely that both France and China will be looking for the political situation to be resolved quickly, and there is a realistic possibility of diplomatic involvement from both Paris and Beijing.
In the immediate future, it is unlikely that any major protests or armed clashes will break out as the Gabonese security forces are seemingly onside, and most indications suggest the public is too. The turning on of the internet was likely a move to win over the public as well as signal a different approach to governance than the Bongo regime. However, this also presents an increased potential for demonstrations and protests, both in favour and against the coup, to occur as information is spread on social media. There is a realistic possibility of sustained demonstrations which will likely lead to disruption in major population hubs. Borders will likely remain closed for upcoming days, but if scenes remain calm, borders are likely to reopen quicker than seen in Niger and Mali.
Advice for travellers affected in Gabon
- Although the coup appears to be relatively peaceful, widespread unrest and violence could ignite at any time. Travellers should avoid all ongoing military activity and any large public gatherings as the security situation may deteriorate quickly and without warning.
- In the event of significant security development, travellers in Gabon should follow any instructions issued by the government or military authorities. If a curfew is declared it is vital to abide by the curfew rules to avoid any conflicts with security forces.
- If violence escalates inside the capital, consider departing from Libreville whilst commercial options are still available.
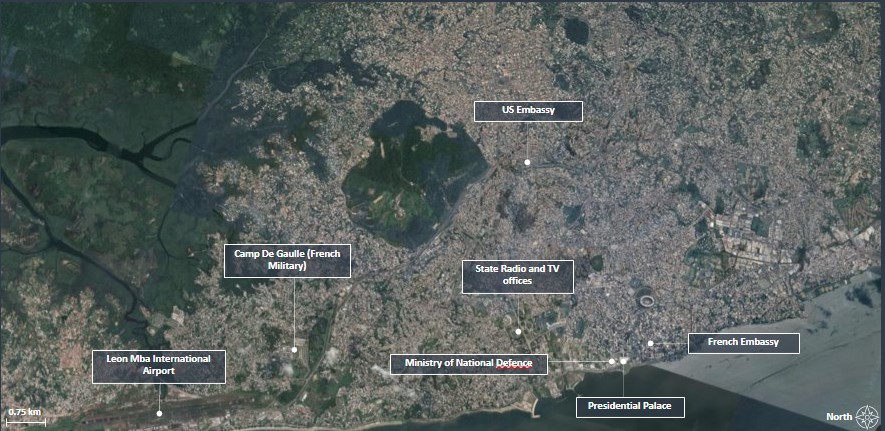
- Key military and political infrastructure inside the capital are very likely to remain focal points for violence and demonstrations. You should be particularly vigilant in these areas and follow any specific advice from the local security authorities.
- Expect significant travel disruption and an enhanced security force posture inside Libreville in the short-term. Should any opposition movement to the coup materialise, it is likely that flights will be suspended, and roadblocks or vehicle checkpoints will be established.
- Always follow all instructions and orders from security forces. Where possible, avoid areas of active conflict and remain inside a secure location away from windows.
- Ensure that you always carry personal identification documents. Consider making photocopies of important documents in case of confiscation, theft or loss and keep these documents separated from the originals.
- Emergency services may be unable to support you in the short-term. Be aware of what consular support may be available to you in-country. Many countries do not provide direct consular support in Gabon. The UK’s consular services for Gabon are based in Yaoundé, Cameroon.
- Have emergency contact numbers saved on your phone. These should include the local authorities, medical facilities and any consular support. Ensure that mobile phones are charged in case of any losses in electricity.
- If caught in the vicinity of a security incident, seek shelter immediately and leave the area if safe to do so. Continue to adhere to all instructions issued by authorities and obey any security cordons in place.
- Monitor the Solace Secure platform and trusted local media for updates relevant to the coup.
